Cervical cancer develops in the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus that connects to a woman’s vagina. It is primarily caused by persistent infection with high-risk strains of the human papillomavirus, a sexually transmitted virus.
Causes of Cervical Cancer
HPV Infection:
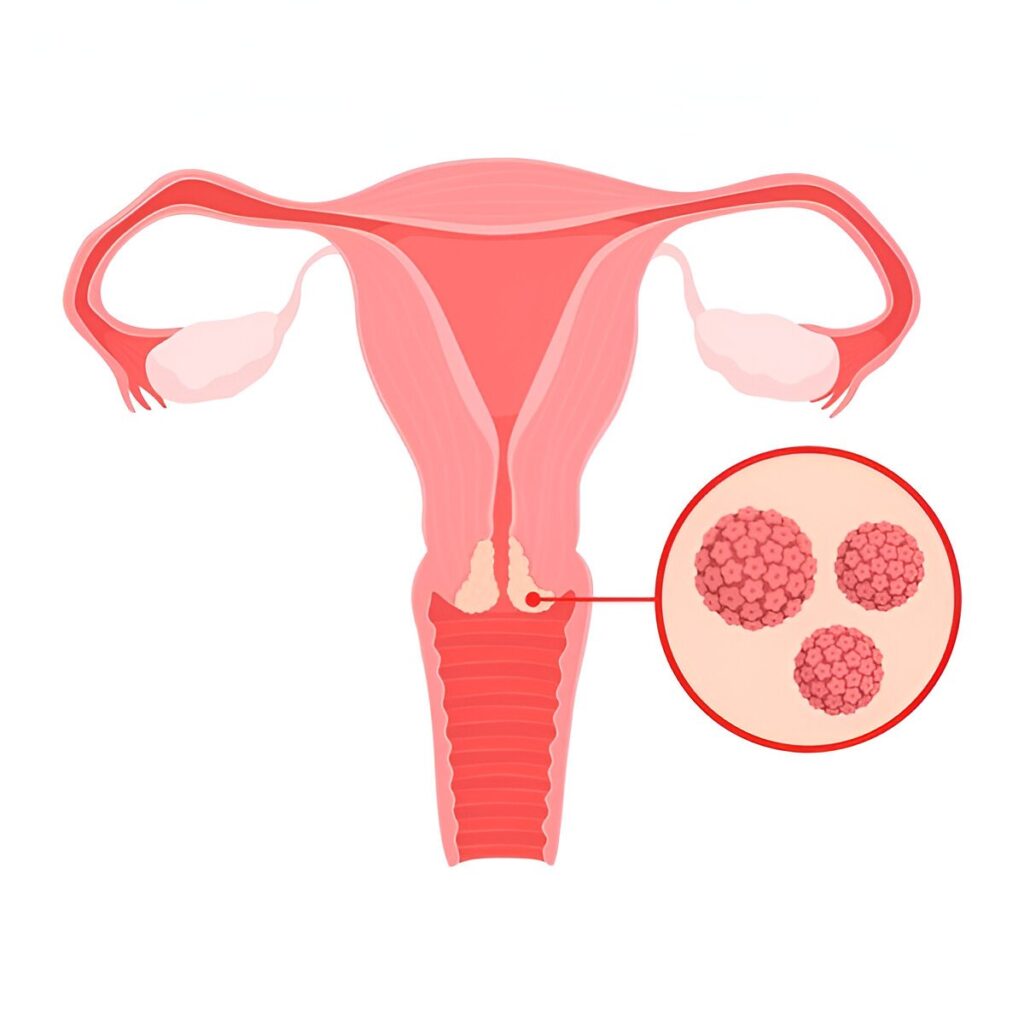
Infection with high-risk strains of HPV is the leading cause of cervical cancer. HPV is a group of viruses that can be transmitted through sexual contact. While most HPV infections resolve on their own, persistent infection with high-risk strains can lead to the development of cervical cancer over time.
Weak Immune System:
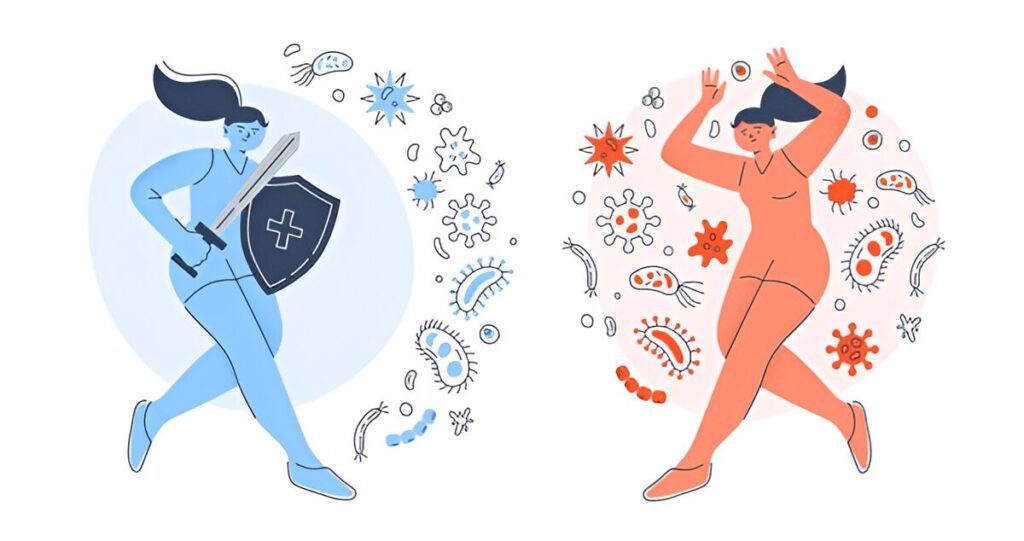
A weakened immune system, often due to conditions such as HIV/AIDS or certain medications, can make it harder for the body to clear HPV infections, increasing the risk of cervical cancer.
Smoking:

Smoking weakens the immune system and can make it more difficult for the body to fight off HPV infections. It also directly damages cervical cells, increasing the risk of cancer development.
Long-term Use of Oral Contraceptives:
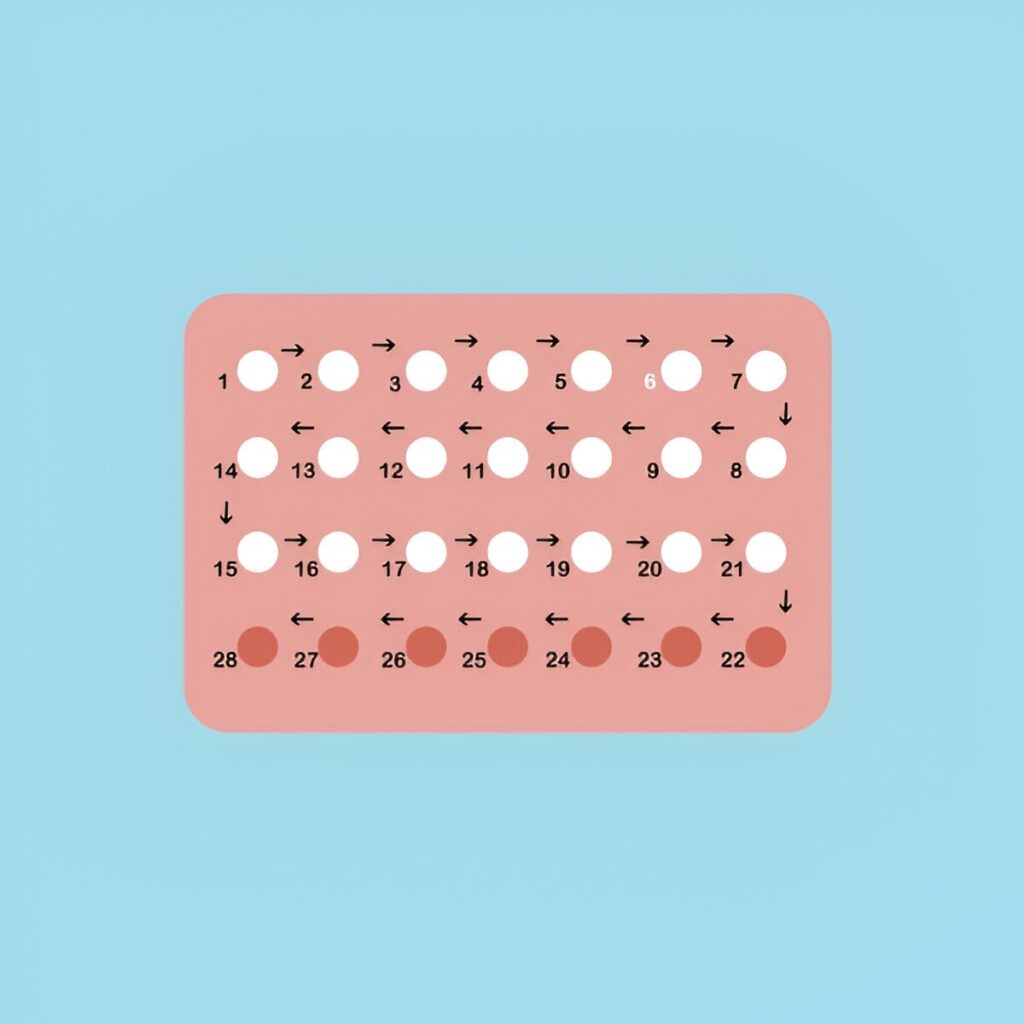
Some studies suggest that long-term use of certain types of oral contraceptives might slightly increase the risk of cervical cancer. However, the risk returns to normal once the pills are stopped.
Prevention Strategies
HPV Vaccination:
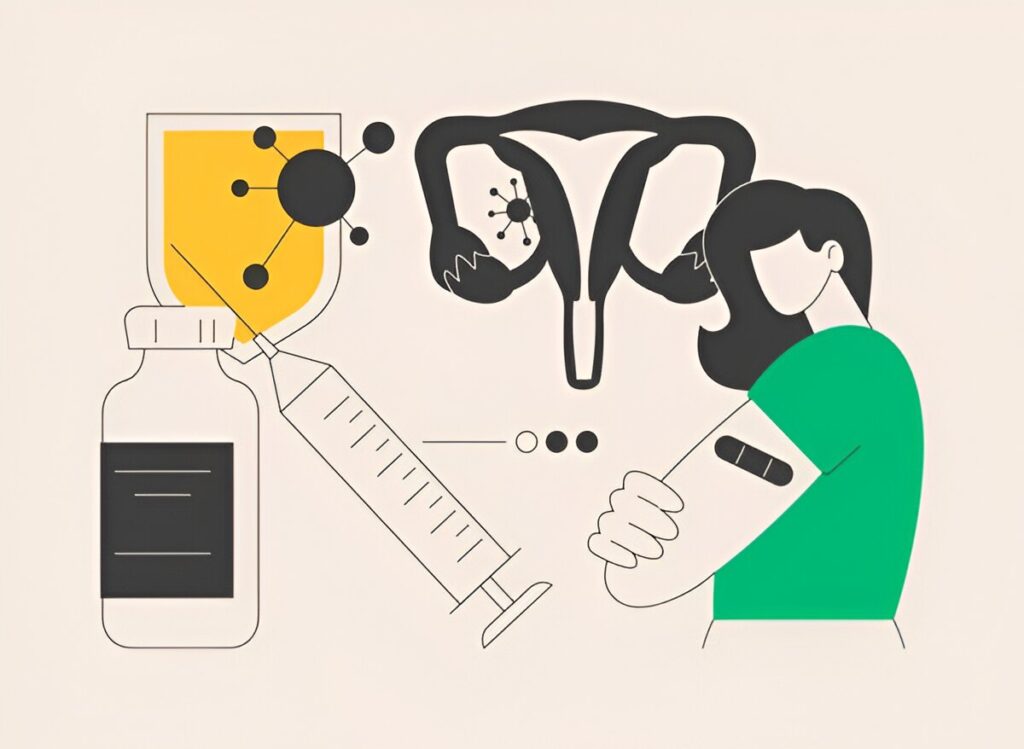

Vaccination is one of the most effective ways to prevent cervical cancer. The HPV vaccine is usually recommended for teenagers as well as for pre-teens before they become sexually active. The vaccine targets the most common high-risk HPV strains and provides protection against cervical cancer and other related cancers.
Regular Pap Smear Tests:
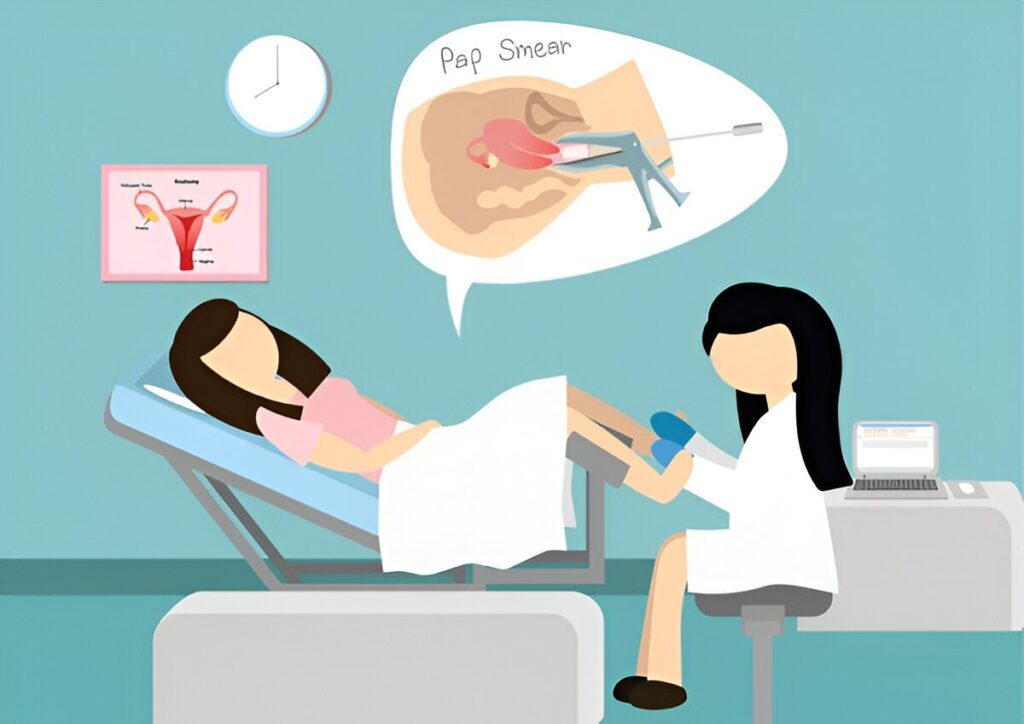
Regular Pap smear tests are crucial for early detection and prevention of cervical cancer. These tests can identify precancerous changes in the cervix, allowing for early treatment and preventing the development of cancer.
HPV Testing:
HPV testing can identify high-risk HPV infections in women. Combined with Pap tests, it can improve the accuracy of detecting cervical abnormalities and precancerous lesions.
Safe Sexual Practices:
Practicing safe sex by using condoms can reduce the risk of HPV transmission.
Quit Smoking:

Quitting smoking not only reduces the risk of cervical cancer but also benefits overall health. So, consider giving up smoking today to lead a healthy and happy life.
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle:

A healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise and stress management can help boost the immune system and reduce the risk of cervical cancer.
Regular Health Check-ups:

Regular visits to a healthcare provider can ensure early detection of any abnormalities or changes in the cervix. It is important to know that early detection and timely treatment significantly improve the prognosis of cervical cancer. Whenever you have concerns about cervical cancer or its prevention, it is always advisable to consult a doctor for the best guidance and advice.



