Malignant melanoma is a type of skin cancer that originates in melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives color to the skin, hair and eyes. Melanoma is considered the most dangerous form of skin cancer due to its potential for aggressive growth and metastasis, which is the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with malignant melanoma is crucial for prevention and early detection. To get the best insights on this condition, refer to DocTube.
Causes of Malignant Melanoma
Ultraviolet Radiation Exposure:
Prolonged and excessive exposure to UV radiation from the sun is a leading cause of melanoma. UV radiation can cause DNA damage in skin cells, leading to the development of cancer. Ultraviolet radiation and cutaneous malignant melanoma. Fair-skinned individuals with less natural protection against UV radiation are at higher risk.
Skin Type and Genetics:
Certain skin types and genetic factors can predispose individuals to melanoma. People with fair skin, light hair, and light eyes are more susceptible because they have less melanin to protect their skin from UV damage. The risk of melanoma also increases when there is a family history of it.
Moles and Atypical Nevi:
The presence of numerous moles, especially atypical or unusual-looking moles can be a risk factor for melanoma. Atypical mole syndrome: risk factor for cutaneous malignant melanoma and implications for management. Any changes in the size, shape, color or texture of moles should be evaluated promptly.
Immune System Suppression:
Individuals with weakened immune systems, either due to medical conditions or medications, are at an increased risk of developing melanoma. A healthy immune system helps the body recognize and fight cancer cells.
Age:
Melanoma can occur at any age, but it is more commonly diagnosed in adults, typically around the age of 50. However, it can also affect younger individuals, especially if they have risk factors. Age as a prognostic factor in patients with localized melanoma and regional metastases.
Gender:
Melanoma is more common in men than in women, possibly due to differences in sun exposure and protective behaviors.
Geographical Location:
The prevalence of melanoma is higher in regions with high UV radiation, such as sunny climates near the equator. However, melanoma can still occur in regions with less direct sun exposure.
Symptoms of Malignant Melanoma
The most common symptoms and signs of malignant melanoma may include the following:
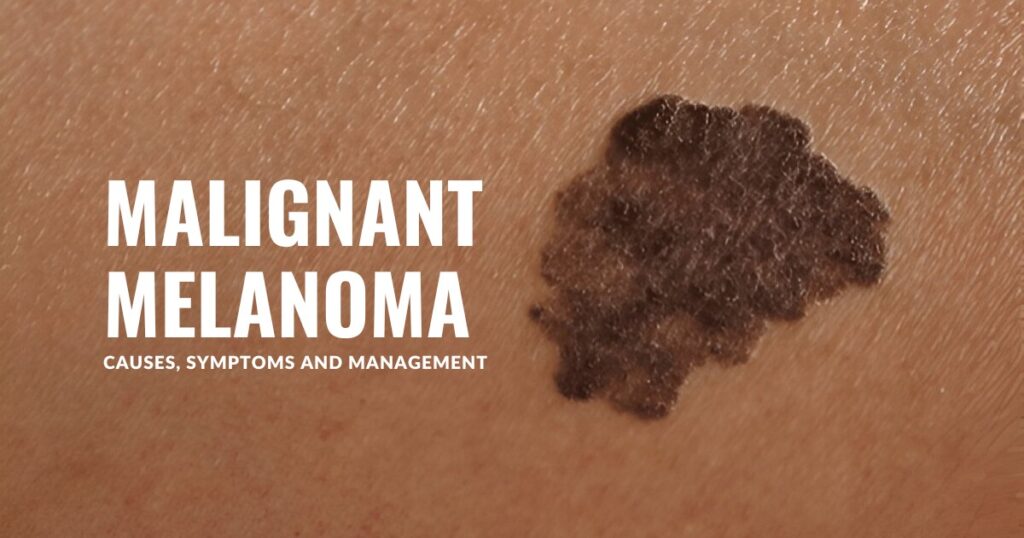
Unusual Moles or New Growths: Malignant melanoma often starts as an atypical or unusual-looking mole. Changes in the size, shape, color or texture of an existing mole or the appearance of a new, irregularly shaped, or multicolored mole should raise suspicion.
Asymmetry:
Another common symptom of malignant melanoma is an asymmetrical lesion or mole wherein one half does not match the other half. Malignant melanoma and the central nervous system. A guide for classification based on the clinical findings. When you draw an imaginary line through the center, the two halves look different.
Irregular Borders:
The edges of the mole are not well-defined and may appear jagged, blurred or irregular.
Color Variation:
Melanomas often have uneven coloring, with shades of brown, black, blue, red or white within the same mole.
Evolving or Changing Moles:
It is important to pay attention to any mole that is changing in size, shape, color or elevation. If a mole evolves or exhibits new symptoms, it may be a warning sign.
Itchiness or Pain:
Some melanomas can become itchy, painful or cause discomfort. Malignant melanoma of the gastrointestinal tract: symptoms, diagnosis, and current treatment options. If a mole suddenly becomes tender or bothersome, it is a reason for concern.
Ulceration or Bleeding:
Melanomas can develop sores that do not heal or may bleed intermittently. These can be an indication of a more advanced melanoma.
Spreading Pigment:
Pigment may spread from the border of a mole into the surrounding skin. This can give the mole a spreading or infiltrating appearance.
Satellite Lesions:
Small, darker spots that appear near the primary mole can be a sign of melanoma’s spread.
Management of Malignant Melanoma
The management of malignant melanoma involves a multi-faceted approach, which typically depends on the stage and extent of the cancer, as well as the individual patient’s overall health. Treatment options for malignant melanoma can include surgery, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy and chemotherapy. The specific treatment plan is determined by the healthcare team after a thorough evaluation. Here are the primary methods used in the management of malignant melanoma:
Surgery:
In case of localized melanoma, surgery is considered to be the primary treatment. The extent of surgery depends on the stage and location of the melanoma. Surgical options may include:
Wide Local Excision:
The removal of the tumor along with some healthy tissue surrounding it. Head and neck malignant melanoma: local recurrence rate following wide local excision and immediate reconstruction.
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy:
This is done to understand whether the cancer has begun spreading to nearby lymph nodes.
Lymph Node Dissection:
The removal of lymph nodes if they are found to contain cancer cells.
Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy is a promising treatment option for advanced melanoma that has spread or cannot be removed through surgery. Immunotherapy in malignant melanoma: recent approaches and new perspectives. It stimulates the patient’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
Targeted Therapy:
Targeted therapy is used when melanoma cells have specific genetic mutations. Medications are used to target these mutations and inhibit the growth of cancer cells.
Radiation Therapy:
Radiation therapy may be used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells, particularly in cases where complete surgical removal is not possible. It can also help relieve symptoms in advanced cases.
Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy is less commonly used for melanoma, as it is generally not as effective as some of the newer treatments. However, it may be considered in cases of advanced melanoma when other options have been exhausted.
Adjuvant Therapy:
Adjuvant therapy is used after surgery to reduce the risk of melanoma recurrence. It may include immunotherapy or targeted therapy, depending on the individual case.
Palliative Care:
For individuals with advanced melanoma that cannot be cured, palliative care focuses on managing symptoms, improving quality of life and providing emotional support.
Can malignant melanoma be cured completely?
In most cases, skin cancers are potentially curable if they are addressed before they spread. However, in cases of more advanced melanoma, the results can be fatal. The sooner malignant melanoma is detected and treated, the higher is the chance of a complete and successful recovery.
What is the most common and significant warning sign of malignant melanoma?
The most important warning sign of malignant melanoma is a new spot on the skin or spots that change in color, size and shape. This spot may look different from the other usual spots on the skin.