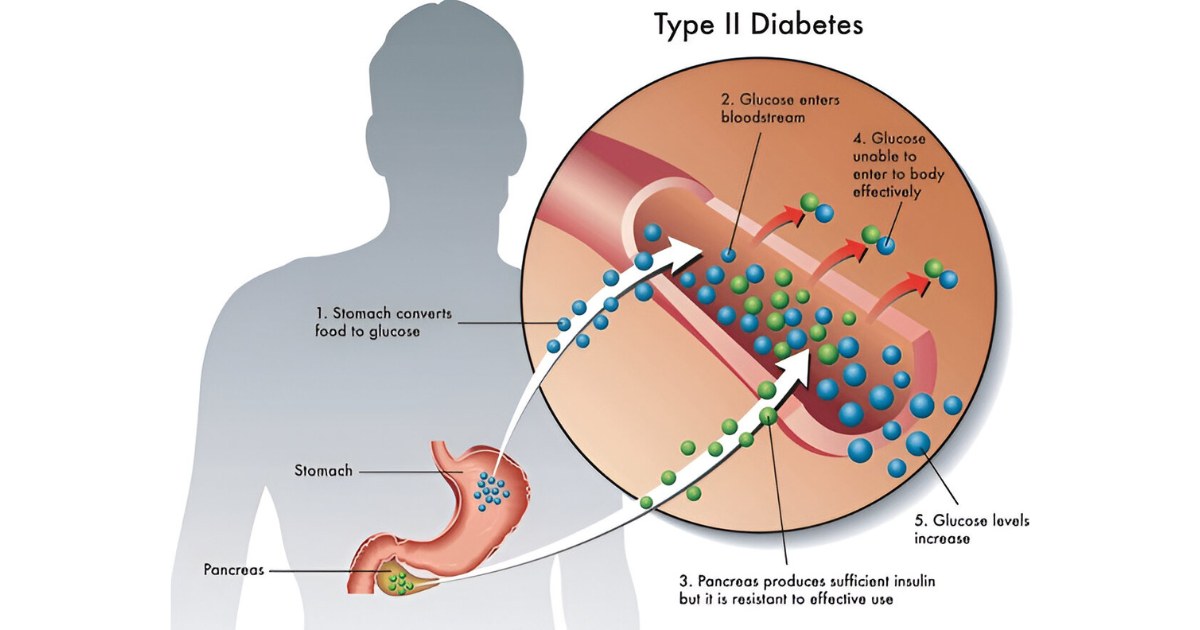
Did you know nearly 37.3 million Americans have diabetes, and many aren’t aware of it? Knowing your normal sugar level is key for good health and can prevent diabetes. Recent research shows that finding abnormal blood sugar levels early can cut the risk of type 2 diabetes by 58%, according to the American Diabetes Association. The World Health Organization (WHO) also reports a rise in diabetes worldwide, from 4.7% in 1980 to 8.5% in 2014, so understanding blood sugar has never been more important.
What Is Normal Sugar Level?
The normal sugar level in the human body is often checked through a fasting blood sugar test, which measures the glucose level in your blood after not eating for 8 hours. This test is the gold standard for diagnosing diabetes and prediabetes. Medical studies show that morning blood sugar levels provide the most accurate reading of how your body manages glucose. According to the Journal of Diabetes Research, the best time for a morning blood sugar test is between 6:00 AM and 8:00 AM. This baseline reading can help doctors spot health issues before they turn serious.
Normal Blood Sugar Ranges
The American Diabetes Association has established guidelines for normal blood sugar levels for adults, based on years of research. Here are the levels and their meanings:
| Blood Sugar Level (mg/dL) | Condition | Implications |
| Below 70 | Hypoglycemia | Immediate attention needed; can lead to confusion if untreated; common in people taking diabetes medicine. |
| 70-99 | Normal Range | Shows healthy insulin function and good overnight glucose regulation; lower risk of heart disease. |
| 100-125 | Prediabetes | Warning sign that suggests a higher diabetes risk; reversible with diet and exercise. |
| 126 or higher | Diabetes | Needs medical care; shows insulin resistance; high risk of complications if untreated. |
Recognizing Blood Sugar Imbalance Signs
When blood sugar levels are not balanced, the body gives clear signs. These low blood pressure symptoms and others can vary depending on whether your blood sugar is too high or too low.
Low Blood Sugar Symptoms
If your blood sugar drops too low, you may experience symptoms such as:
- Shaking and sweating that can come on suddenly
- Confusion and trouble focusing
- Intense hunger and moodiness
- Dizziness, which can make balancing hard
- Fast heartbeats, often felt as a flutter
- Weakness, which can make simple tasks harder
High Blood Sugar Symptoms
Signs of high blood sugar may include:
- Constant thirst that drinking doesn’t satisfy
- Needing to urinate often, especially at night
- Blurred vision that comes and goes
- Feeling very tired even after resting
- Unexplained weight loss despite eating normally
- Cuts and wounds that take a long time to heal
Tips for Keeping Your Blood Sugar Levels Healthy
Studies from the Journal of Diabetes Research reveal that people who follow these tips can reduce their diabetes risk by 40%. Here’s how to keep your normal sugar level steady:
Morning Routines
Starting your day with healthy habits helps manage blood sugar:
- Eat breakfast within two hours of waking up.
- Include protein and fiber in your first meal.
- Drink water to stay hydrated.
- Do some light exercise in the morning.
- Check your blood sugar if your doctor recommends it.
Physical Activity
Exercise has been shown to improve how the body uses insulin:
- Aim for 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly.
- Try both cardio (walking, swimming) and strength training.
- Take short walks after meals (15-20 minutes).
- Stay active throughout the day.
- If you have diabetes, check blood sugar before and after exercising.
Healthy Eating
Eating well has a major impact on blood sugar:
- Focus on high-fiber foods (try for 25-30g daily).
- Choose whole grains rather than refined carbs.
- Eat lean proteins in every meal.
- Add healthy fats like avocados and nuts.
- Keep portion sizes reasonable.
Blood Sugar Testing Guidelines
How often you test depends on your health needs:
- Annual testing for healthy adults.
- Quarterly tests for people with prediabetes.
- Daily testing for diabetics (frequency varies).
- Additional tests during illness or stress.
- Special testing for pregnant women.
Age-Specific Blood Sugar Tips
Different age groups have unique blood sugar needs and concerns:
Children and Teenagers
- Normal range: 70-110 mg/dL
- More frequent testing during growth spurts
- Additional tests when sick
- Special care for blood sugar control during sports or physical activity
Older Adults
- Acceptable range: 100-110 mg/dL
- Prone to low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia
- Need regular testing if taking medications
- May need adjusted treatment goals for safer management
Taking Charge of Your Health
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), people who regularly check their blood sugar are 40% more likely to keep it in a healthy range. The American Diabetes Association also says that catching prediabetes early can reduce the chance of developing type 2 diabetes by 58%.
While this information provides a good foundation for understanding blood sugar, always talk to your doctor for specific advice. They can help interpret your blood sugar numbers and create a plan that’s right for you.
Conclusion
Controlling your normal sugar level is more than just avoiding diabetes—it’s about living a healthy, long life. Regular blood sugar checks, eating balanced meals, and staying active can help keep your blood sugar in a healthy range and improve your overall well-being. Remember, adding these healthy habits to your routine can make a big difference in your health journey.