Breast cancer accounts for 14% of female cancer cases in India. Though anybody may have it, women over 40 are more likely to. Understanding this condition may help individuals take the appropriate precautions despite its scariness.
Breast cancer is caused by uncontrolled cell growth. A lump or bulk of these cells is generally the first symptom. Sometimes, individuals detect changes in their breast or nipple appearance. This page covers all aspects of breast cancer, from origins and symptoms to stages and treatments. Breast cancer awareness is crucial since early diagnosis may save lives. Many survivors may live healthy lives following treatment with proper care.
Let us learn about breast cancer so everyone can remain informed and act.
What is Breast Cancer?
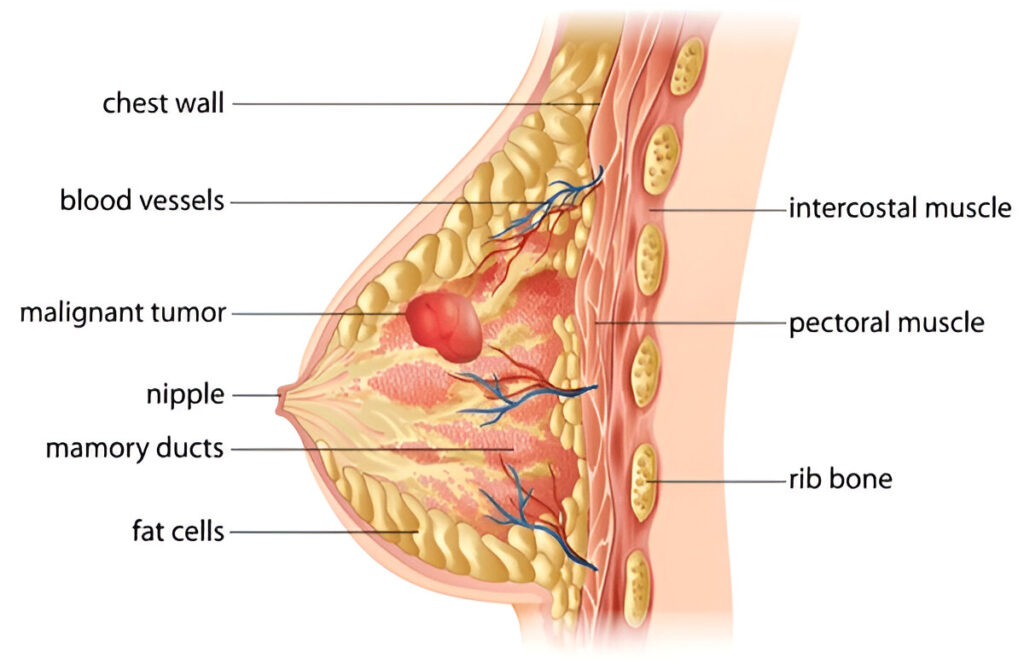
Breast cancer begins in breast tissue. A lump or tumor forms when breast cells develop uncontrolled. These cancer cells may infect surrounding tissues, making breast cancer aggressive. Non invasive or in situ cancer remains in the breast where it began and does not spread. Untreated, non invasive cancer may turn invasive.
Breast cancer mainly affects women, although males may get it. Women are more likely to have it. Breast cancer accounts for 25% of all female cancer cases, according to the WHO. It accounts for 14% of female malignancies in India. Men can get breast cancer, although their chances are reduced due to smaller breast tissue.
Knowing the distinction between invasive and non invasive breast cancer helps physicians select therapy. Regular screenings and awareness may help detect breast cancer early when it is most curable. This is why everyone, particularly women, should understand about breast cancer development and spread.
Breast Cancer Symptoms
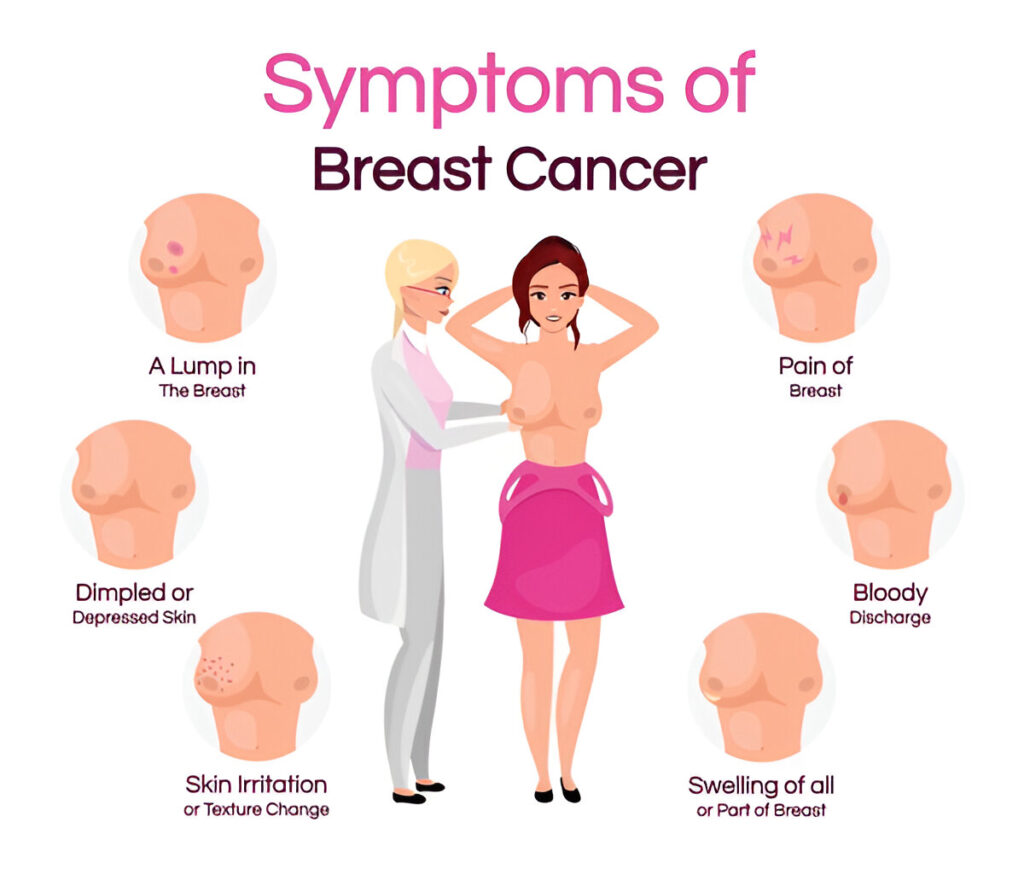
Various people have various breast cancer symptoms. However, there are several typical indications everyone should recognize. Early detection saves lives, so watch for bodily changes.
Lump or Mass in the Breast or Armpit
Lumps or masses in the breast or under the arm are the most prevalent breast cancer symptoms. These bumps are generally firm and harmless, although some may hurt. Check for odd lumps, which may indicate a problem.
Swelling, Pain, or Changes in the Breast or Nipple
A typical symptom is breast or armpit swelling or discomfort. Also, look for changes in breast size or form. The nipple may invert or generate non breastfeeding related discharge.
Skin Changes
Dimpling, redness, and thickness may result from breast cancer. The skin may resemble an orange peel or have unique textures. These alterations may suggest breast tissue issues.
What Causes Breast Cancer?
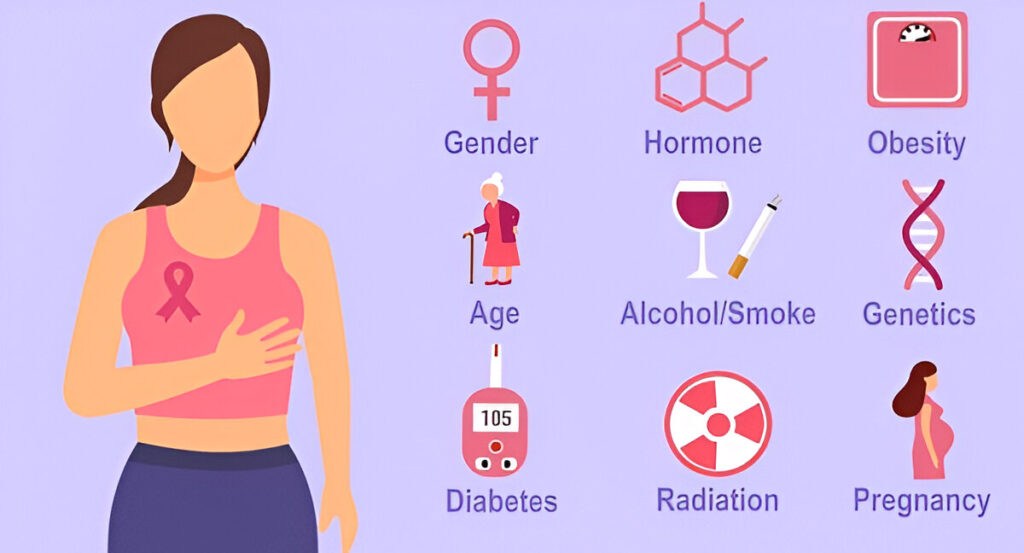
Breast cancer may affect everyone, but several variables increase its risk. Understanding these may minimize risk and help individuals see what increases breast cancer risk.
Genetic Factors
Genetic abnormalities often cause breast cancer. Some individuals inherit breast cancer causing gene mutations from their parents. The most famous breast cancer genes are BRCA1 and BRCA2. Mutations in these genes increase breast and ovarian cancer risk. Mutations in TP53 also raise breast cancer risk. Having a family member with breast cancer, particularly a young one, increases your risk.
Hormonal Factors
Hormones also cause breast cancer. Early periods, late menopause, and HRT may increase estrogen exposure and risk. Estrogen causes breast cells to grow, which may lead to cancer if unchecked.
Lifestyle and Environment
We cannot control our genes, but lifestyle decisions may raise breast cancer risk. Being overweight or obese, particularly after menopause, increases risk because fat cells release more estrogen. Regular drinking might also cause breast cancer. Another possibility is radiation exposure, such as radiation treatment for another malignancy.
Risk Factors
- Age: Breast cancer risk rises with age. The American Cancer Society reports that most breast cancers are detected in women over 50.
- Ethnicity: Various ethnicities suffer from breast cancer differently. Black women are more likely to have aggressive breast cancer, according to research.
- Family History: Your risk increases if your mother or sister has breast cancer. Genetic mutations may increase cancer risk.
Types of Breast Cancer
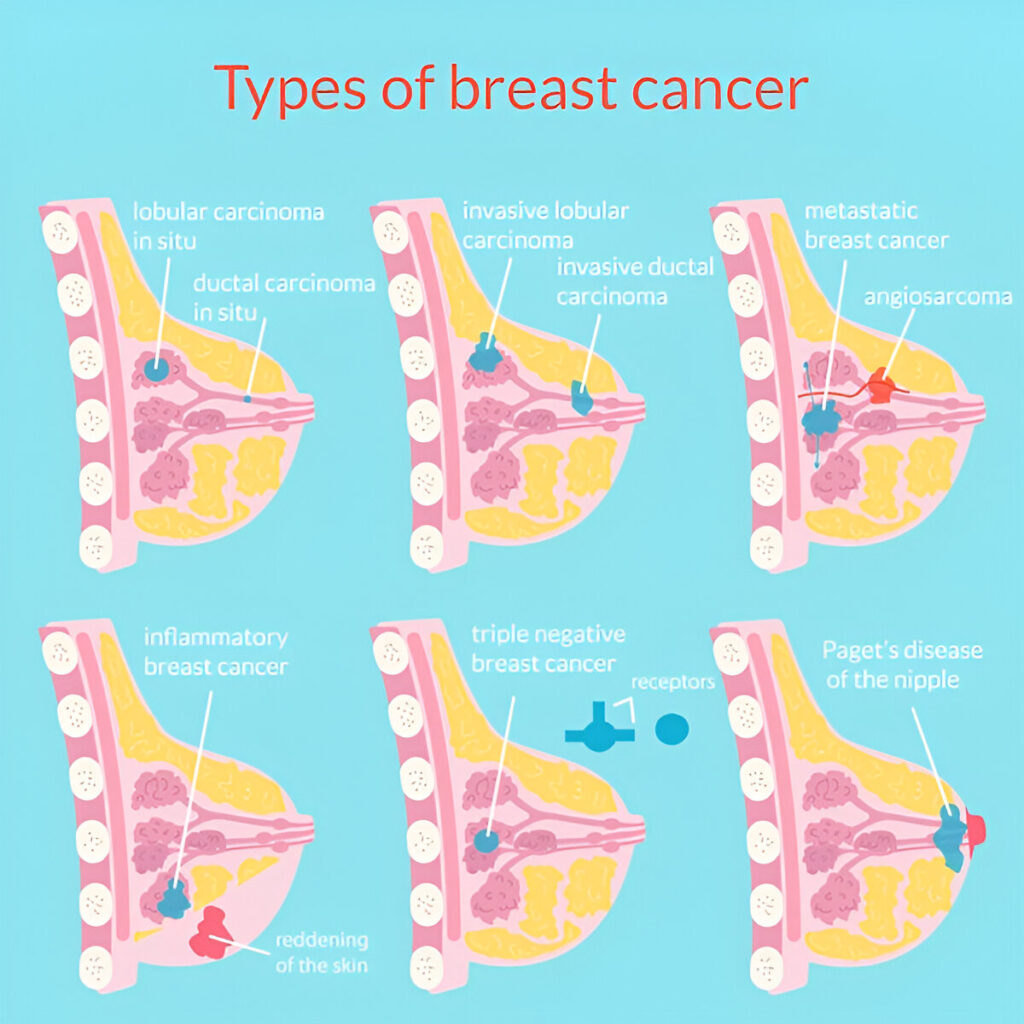
Multiple diseases cause breast cancer. Breast cancer starts and spreads differently in different forms. Knowing the breast cancer kind helps physicians choose a therapy.
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS)
DCIS is a non invasive breast cancer. This indicates that the milk duct cancer cells have not migrated to adjacent tissues. Treatment is frequently available for DCIS, an early breast cancer. Untreated, it may become an invasive cancer.
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC)
IDC is the most frequent invasive breast cancer. This kind extends from the milk ducts to other breast tissue. Early diagnosis is crucial since IDC may spread via the blood or lymph nodes.
Lobular Carcinoma
Lobular carcinoma starts in milk gland lobules. It might be invasive or non invasive. Invasive lobular carcinoma is second behind IDC in breast cancer prevalence.
Rare Types of Breast Cancer
Inflammatory and triple negative breast cancers are uncommon. Aggressive inflammatory breast cancer generates red and swollen breasts. Triple negative breast cancer is resistant to hormonal and targeted therapy, making treatment challenging.
Stages of Breast Cancer
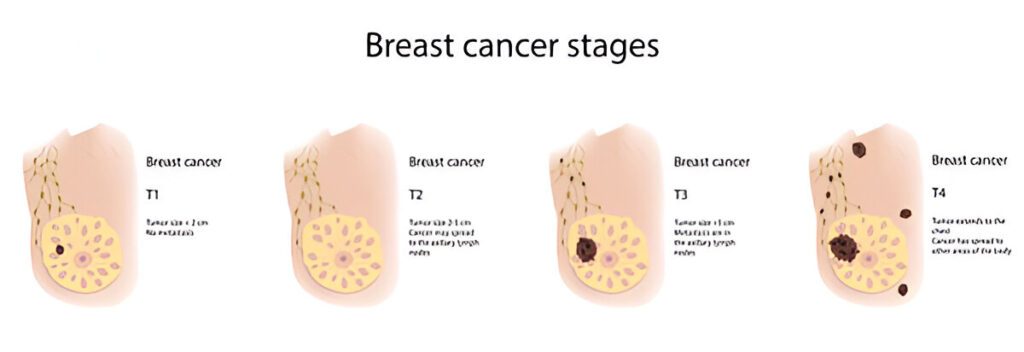
Breast cancer is staged to assist physicians in identifying its spread and treatment. TNM staging is used to define stages of breast cancer. TNM stands for tumor, node, and metastasis.
TNM System Explained
- T (Tumor size): Breast tumor size. Small to giant tumors effect the cancer stage.
- N (Node involvement): This indicates if cancer has spread to adjacent lymph nodes, especially beneath the arm.
- M (Metastasis) indicates whether the cancer has spread to the bones, liver, lungs, or brain.
These characteristics divide breast cancer into five stages, from Stage 0 to Stage IV.
Stage 0: Non invasive Cancer
Stage 0 breast cancer is non invasive Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS). Milk duct cancer has not spread to breast tissue. The early stage is generally curable with early intervention.
Stage I: Small Tumor, Limited Spread
Stage I tumors are up to 2 cm and may or may not have migrated to lymph nodes. Early breast cancer therapy is typically adequate.
Stage II: Larger Tumor or Lymph Node Involvement
Two substages comprise Stage II:
- Stage IIA: The tumor is tiny but has migrated to adjacent lymph nodes or 2–5 cm but has not.
- Stage IIB: The tumor is beyond 5 cm and may have migrated to the lymph nodes.
Stage III: Locally Advanced Cancer
Cancer has progressed to numerous surrounding lymph nodes and maybe the chest wall or skin in Stage III. The tumor may exceed 5 cm. This stage is locally advanced but curable with vigorous treatment.
Stage IV: Metastatic Breast Cancer
Stage IV breast cancer, sometimes called metastatic breast cancer, has gone to the lungs, liver, bones, or brain from the breast and adjacent lymph nodes. Though more challenging to cure, several medicines may manage Stage IV breast cancer and improve quality of life.
Breast Cancer Diagnosis
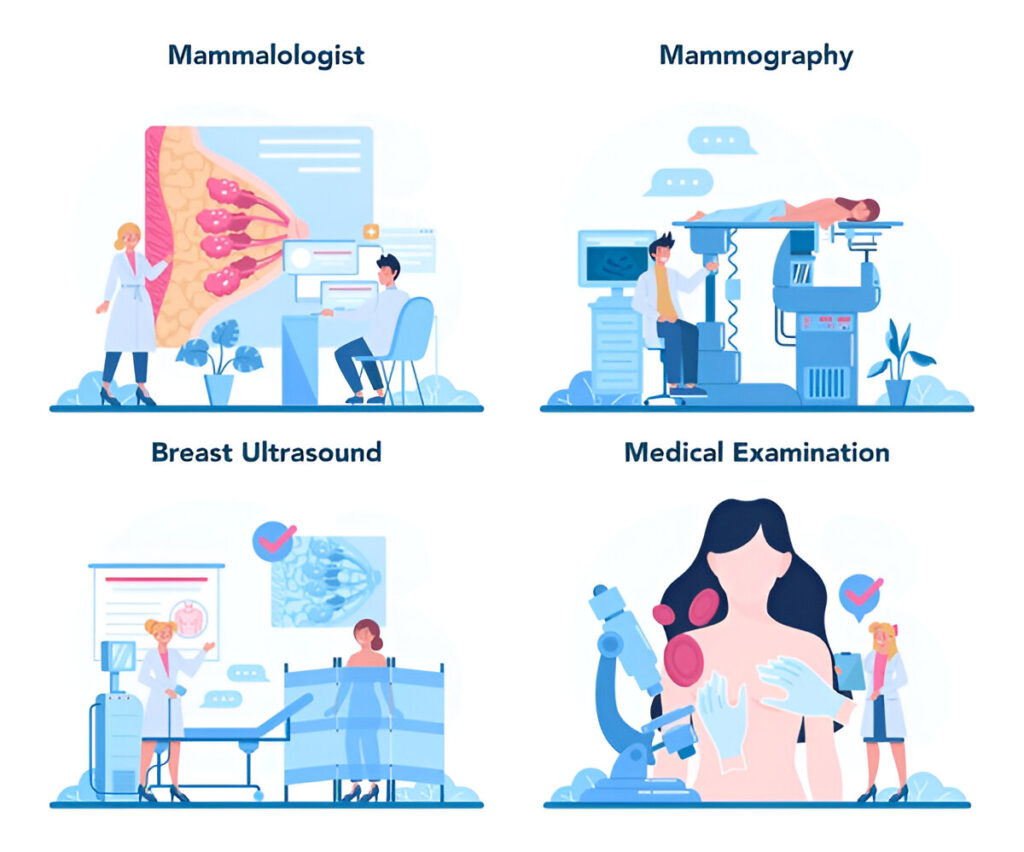
Breast cancer diagnosis requires many tests to identify and stage the disease. Effective therapy requires early diagnosis. Doctors utilize these breast cancer diagnostic tools:
Mammograms
Mammograms are the most prevalent early breast cancer screening method. Breast X rays let physicians identify tumors or abnormalities before they may be felt. Women over 40 should have mammograms for early, curable breast cancer detection. The WHO estimates that mammograms may decrease breast cancer mortality by 20 to 30% in women aged 50 to 69.
Ultrasounds and MRIs
Doctors may employ ultrasound or MRI to investigate abnormal mammograms. An ultrasound determines whether a mass is solid or fluid, whereas an MRI shows malignant spots that other tests may miss.
Biopsies
If imaging shows malignancy, a biopsy is subsequent. This treatment involves removing a tiny breast tissue sample for lab testing for cancer cells. Depending on the cancer’s location, needle or surgical biopsies are performed.
Genetic Testing
Doctors may offer genetic testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2, which significantly increase breast cancer risk. This test may help people with a family history of breast cancer recognize their risk and avoid it.
Consult a doctor about any symptoms to improve treatment results.
How Is Breast Cancer Treated?
Cancer kind, stage, and patient health determine breast cancer therapy. Doctors typically mix different treatments to develop a specific treatment plan for the most outstanding results.
Surgery
Surgery is generally the initial breast cancer treatment. Two primary types:
- Lumpectomy: This breast conserving operation removes just the tumor and some surrounding tissue.
- Mastectomy: Removes the whole breast. Afterward, reconstructive surgery may restore breast form.
Radiotherapy
After surgery, radiation kills any leftover cancer cells. It is often utilized to prevent cancer recurrence following lumpectomy. Radiation may be used after mastectomy if the malignancy is significant or has spread to the lymph nodes.
Chemotherapy
Drug based chemotherapy kills cancer cells. It may reduce the tumor before surgery (neoadjuvant treatment) or eliminate cancer cells after surgery (adjuvant therapy). Breast cancer that has spread is treated with chemotherapy.
Hormone Therapy
Estrogen and progesterone sensitive malignancies respond to hormone treatment. Tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors prevent these hormones from increasing cancer. Recurrence is reduced by hormone treatment after surgery, but it might also diminish tumors before surgery.
Targeted Therapy
HER2 protein increases the aggressiveness of certain breast tumors. Trastuzumab (Herceptin) targets HER2 positive cancer cells. Together with chemotherapy, these medications enhance treatment results.
Personalized Treatment Plans
Every breast cancer case is distinct; thus, physicians customize treatment strategies. Treatment effectiveness depends on the cancer stage, kind, and patient condition. Early stage tumors may merely need surgery and radiation, but advanced cancers may require surgery, chemotherapy, hormone, or targeted treatments.
Breast Cancer Prevention

Breast cancer cannot be prevented, but there are measures to lower your risk. Prevention and healthy living may reduce your risk of breast cancer.
Consuming Less Alcohol
Drinking alcohol increases breast cancer risk. Alcohol use increases the danger. Drinking one alcoholic drink a day increases the risk of breast cancer by 7 to 10%, according to research.
Healthy Weight Maintenance
Being overweight or obese, particularly after menopause, increases breast cancer risk. Breast cancer may arise due to excess estrogen from fat tissue.
Regular exercise
Another breast cancer prevention tip is being active. The American Cancer Society suggests 150 minutes of moderate or 75 minutes of strenuous weekly exercise. Physical exercise can prevent breast cancer by maintaining a healthy weight.
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding may reduce breast cancer risk for people who can. The protective benefit of breastfeeding increases with time.
Prevention Surgery for High Risk Patients
Doctors may propose preventative procedures for women with BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations. This may include a mastectomy or oophorectomy. These operations considerably lower breast cancer risk.
Breast Cancer Survival Rates and Prognosis
Breast cancer survival rates depend on kind and early detection. Around 99% of early stage breast cancer patients survive 5 years globally. This%age reduces to 27% for Stage IV or metastatic breast cancer, which has spread. These data emphasize early detection and treatment.
Early identification of breast cancer in India is challenging, yet survival rates are rising. The ICMR estimates a 60 to 70% 5 year survival rate for urban breast cancer. Rural places have worse survival rates because of later stage diagnosis and insufficient treatment.
Factors Affecting Prognosis
Breast cancer prognoses depend on many factors:
- The stage at Diagnosis: A stage is the most crucial element in cancer diagnosisge. Stage 0 and Stage I malignancies have more excellent survival rates than stages III and IV.
- Type of Breast Cancer: For instance, triple negative breast cancer is more aggressive and more challenging to cure, which may lower survival chances.
- Response to Treatment: How effectively chemotherapy, radiation, or hormone therapy work for cancer may affect the result. Survival improves with personalized treatment strategies based on cancer features like HER2 status.
Breast cancer survival rates worldwide and in India depend on frequent screenings, early detection, and efficient treatment.
Conclusion
Early breast cancer diagnosis saves lives. Regular mammograms and awareness of breast cancer signs help detect the illness early when therapy is most successful. Early detection is crucial since early stage breast cancer has a 99% 5 year survival rate, but later stages have a much lower rate.
Talk to your doctor about your risk factors, particularly if you have a family history of breast cancer or BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations. Based on your risk, your doctor may prescribe screening alternatives and frequency. Frequent checkups and lifestyle adjustments may improve the prevention and management of breast cancer.
Common Breast Cancer Questions and Answers
What are the early signs of breast cancer?
A lump in the breast or underarm, changes in breast size or form, nipple discharge, or skin changes like redness or dimpling may indicate breast cancer. These symptoms should be reported to a doctor for early detection.
Can men get breast cancer?
Men may acquire breast cancer, although rarely. About 1% of breast cancer cases are male. Men should examine for breast lumps or changes and seek medical help if necessary.
How often should I get screened for breast cancer?
Mammograms should begin around 40 and be repeated every 1 to 2 years, depending on risk factors. Your doctor might recommend a screening regimen depending on your age and family history.
Does having a family history of breast cancer increase my risk?
A family history of breast cancer, particularly in close relatives like a mother or sister, raises your risk. Gene mutations like BRCA1 or BRCA2 may also increase breast cancer risk.
What is the survival rate for breast cancer in India?
Breast cancer has a 60 to 70% 5 year survival rate in India, particularly in metropolitan regions with better early identification and treatment. Rural communities have worse survival rates owing to delayed diagnosis and insufficient treatment.