Liver transplantation is a life-saving medical procedure that becomes a necessity when individuals face advanced liver disease and when conventional treatments are no longer effective. The decision to undergo a liver transplant is a complex one, requiring careful evaluation of various factors by both medical professionals and patients.
When is liver transplantation considered?
Advanced Liver Disease:
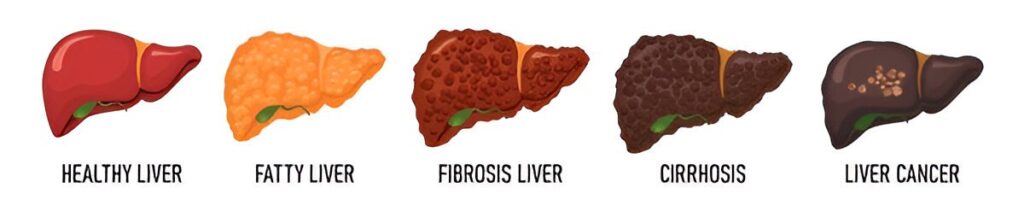
Liver transplantation is typically considered when a person’s liver disease reaches an advanced stage, often referred to as end-stage liver disease. This is characterized by severe liver damage, leading to significant impairment of liver function. Common causes include chronic viral hepatitis, cirrhosis, alcoholic liver disease and certain genetic disorders.
Declining Liver Function:
Persistent deterioration in liver function despite medical intervention and lifestyle changes may signal the need for a transplant. Indications for liver transplantation. This is often evidenced by worsening laboratory values and clinical symptoms.
Complications of Cirrhosis:
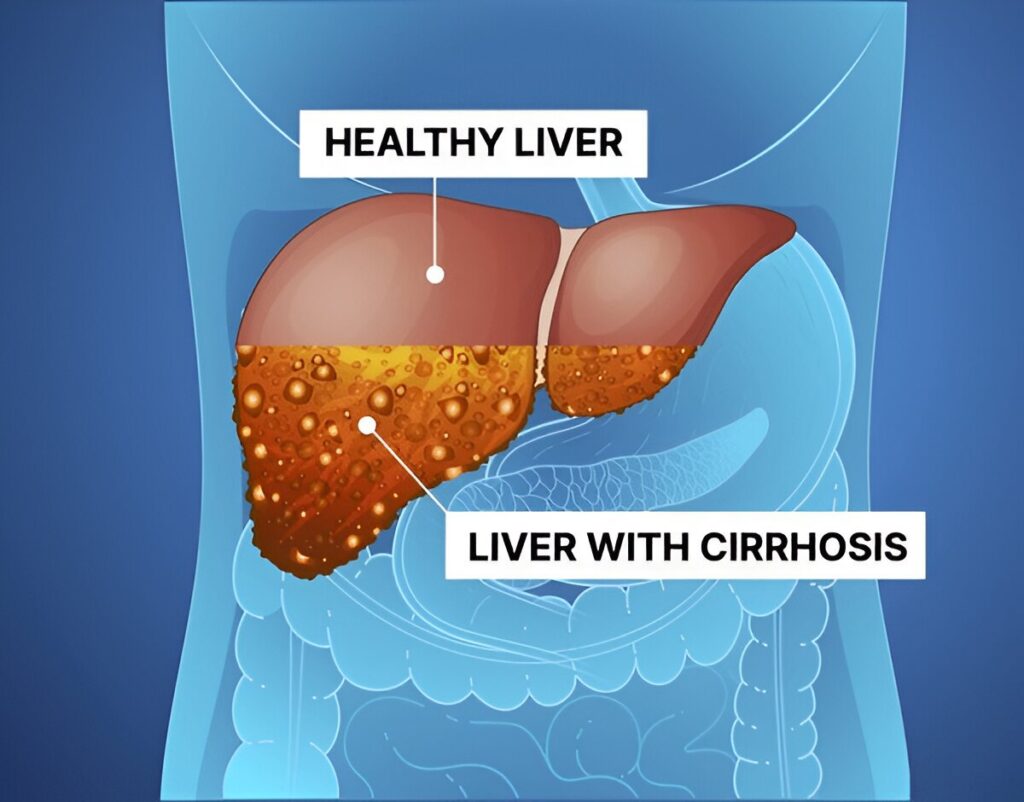
Individuals experiencing complications of cirrhosis, such as ascites or accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, hepatic encephalopathy wherein the patient experiences confusion and altered consciousness or has variceal bleeding, may be ideal candidates for transplantation.
Failure of Medical Management:
When medical therapies fail to control the progression of liver disease, transplantation becomes a viable option. Medications and other interventions may provide temporary relief, but they may not address the underlying issue in advanced stages.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma:
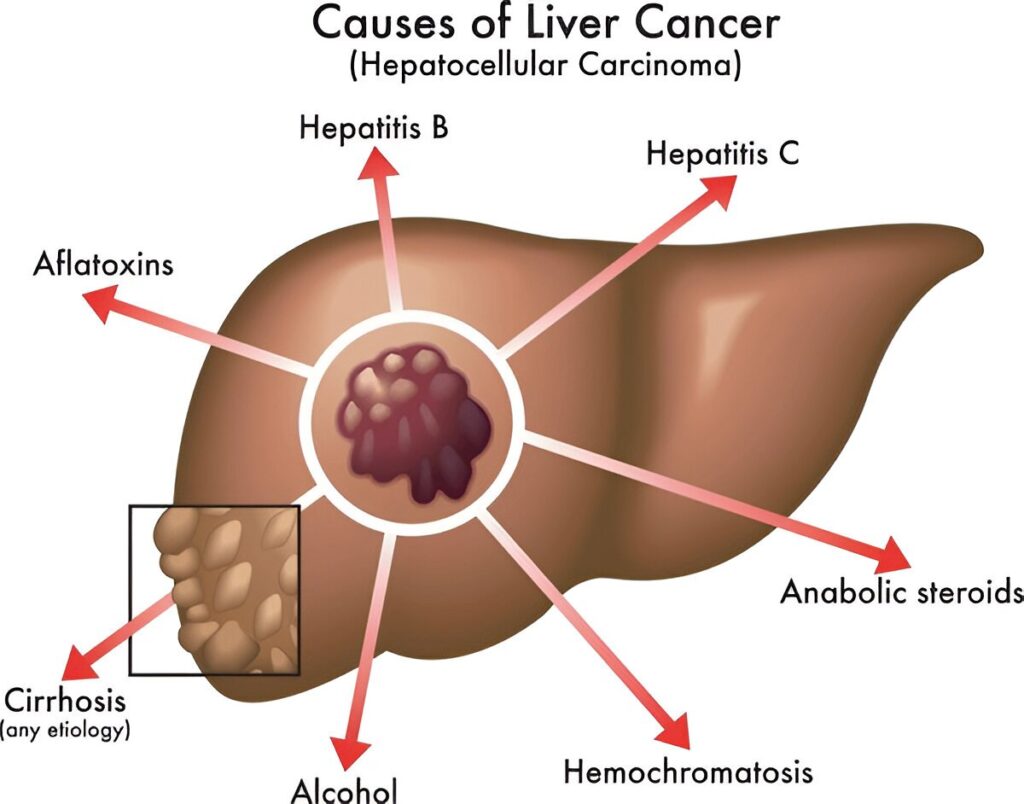
Liver transplantation is considered for individuals with hepatocellular carcinoma, a type of liver cancer. Meeting specific criteria, such as tumor size and number, is essential for transplant eligibility.
Quality of Life:

The impact of liver disease on a person’s quality of life is a crucial consideration. Persistent symptoms, fatigue and a reduced ability to perform daily activities may prompt the consideration of transplantation.
Care Tips To Follow After Liver Transplantation
Medication Adherence
Take immunosuppressant medications as prescribed by your doctor. These medications prevent your immune system from rejecting the new liver. Follow the prescribed schedule and dosage meticulously. Missing doses or altering the regimen without medical guidance can jeopardize the success of the transplant.
Regular Medical Check-ups

Scheduled follow-up appointments must never be missed with the transplant team. These visits are crucial for monitoring your progress, adjusting medications and addressing any emerging issues.
Infection Prevention

In order to minimise the risk of infections, practice good hygiene such as regular handwashing and maintaining cleanliness. Avoid close contact with individuals who are sick and promptly report any signs of infection, such as fever or persistent cough to your doctor.
Diet and Nutrition

Follow a well-balanced and nutritious diet. A healthy diet promotes healing and helps prevent complications. Limit sodium intake to prevent fluid retention, a common issue after transplantation. Monitoring your weight regularly can help identify any fluid-related concerns.
Physical Activity

As per the doctor’s guidance, resume physical activities. Regular exercise promotes overall well-being and aids in the recovery process. A randomized trial of exercise and dietary counseling after liver transplantation. Avoid strenuous activities initially and consult your healthcare team before starting any new exercise regimen.
Hydration

Stay adequately hydrated, but be mindful of fluid restrictions, if any. Proper hydration supports liver function and helps prevent complications such as kidney problems.
Alcohol and Substance Avoidance

Completely abstain from alcohol and avoid recreational drugs. These substances can negatively impact the new liver and interact with medications.
Emotional and Mental Well-being

Whenever needed, seek proper support from your friends, family and mental health professionals. The post-transplant period can be emotionally challenging and having a strong support system is crucial. Report any signs of depression, anxiety or changes in mood to your healthcare team.
Education and Communication

Stay informed about your condition, medications and potential warning signs. Quality of life before and after liver transplantation for cholestatic liver disease. Understanding the transplant process empowers you to actively participate in your recovery. It is also important for you to communicate with your doctor and healthcare team openly regarding changes or concerns regarding your health.
Liver Transplant Cost in India
Liver transplant cost in India can vary depending on several factors, including the hospital, surgeon’s fees, the patient’s medical condition and post-operative care. On average, the cost of a liver transplant in India ranges from 10,00,000 and 28,00,000.
India has gained recognition for its world-class medical infrastructure, experienced transplant surgeons and state-of-the-art facilities, making it a preferred destination for medical tourists. The availability of skilled healthcare professionals, advanced technology and internationally accredited hospitals contribute to the success of liver transplant surgeries in the country.
FAQs
Is there an age limit for liver donation?
The preferred age limit for liver donation is 18-60 years.
Can a family member donate the liver?
In cases where a liver transplant candidate is eligible to receive from a living donor, a family member or relative may be considered for donation.